‘Tis the Season, as they say, for one’s Easter Duty. Including everyone’s least favorite sacrament.
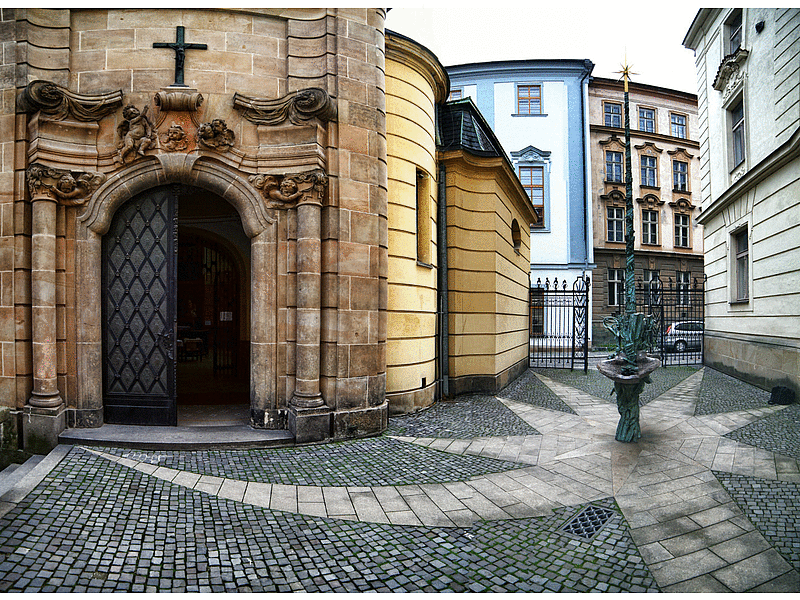
The Neo-baroque chapel of St. John Sarkander is a two-storeyed building crowned with a dome with a lantern opening. In the middle of the chapel, there is a circular opening into the basement, where a torture rack from Sarkander’s time has been situated. The interior of the chapel is impressively illuminated. Daylight from the lantern opening penetrates through the circular hole in the floor down to the basement.
The immediate surroundings of the chapel are one of the most picturesque corners of Olomouc, Moravia, Czech Republic. The adjoining double staircase is graced by a statue of St. John of Nepomuk, in a corner niche there is a statue of St. Jan Sarkander.
In the past, the city prison where John Sarkander was interrogated and tortured to death in 1620 was located on the site of the Chapel. John Sarkander was accused by Protestants of having helped to arrange the invasion of the army of the Polish Catholic King into Moravia. However, he did not violate the Seal of Confession during the torture.
Son of Georg Mathias Sarkander and Helene Kornicz Sarkander. Born in a time and place in the midst of the turmoil of the Protestant Reformation. His father died when Jan was still young, and the family moved to Pribor. He married, but his wife died when they were young, and they had no children.
Educated by Jesuits at Prague, receiving a master of philosophy degree in 1603. In Olmutz, he became the center of a struggle for the hearts and souls of the local people; he was supported by Baron von Labkowitz of Moravia, but bitterly opposed by the wealthy anti-Catholic landowner Bitowsky von Bystritz.
The year 1618 saw the start of the Thirty Years War between Catholic and Protestant armies. When Protestant forces occupied Hollenschau, Jan was briefly exiled to Poland, but returned to minister to his oppressed parish flock. Polish forces moved into the area in 1620, and battle seemed imminent. Jan visited the field commander, carrying the Blessed Sacrament in a monstrance as a shield and chastisement. No battles were fought in the area of Hollenshau.
Seizing the opportunity to brand him a spy, and thus explain the lack of attack by the Polish troops, his enemy von Bystritz denounced Father Jan as a traitor. Jan was arrested, taken to Olmütz, and tortured for a confession, for revenge, and to get him to break the seal of the confessional and supply damaging information about his patron and parishioner Baron von Labkowitz. Sarkander was racked, beaten and murdered, but he clung to his faith and gave his tormentors nothing. He was racked on February 13, 17, and 18th. His tendons burst. His bones dislocated. On each of the days mentioned, the torture lasted for two and three hours, lighted candles and feathers soaked in oil, pitch, and sulphur were strewn over his body and ignited.
The sacramental seal is inviolable. Quoting Canon 983.1 of the Code of Canon Law, the Catechism states, “…It is a crime for a confessor in any way to betray a penitent by word or in any other manner or for any reason” (No. 2490). A priest, therefore, cannot break the seal to save his own life, to protect his good name, to refute a false accusation, to save the life of another, to aid the course of justice (like reporting a crime), or to avert a public calamity. He cannot be compelled by law to disclose a person’s confession or be bound by any oath he takes, e.g. as a witness in a court trial. A priest cannot reveal the contents of a confession either directly, by repeating the substance of what has been said, or indirectly, by some sign, suggestion, or action. A Decree from the Holy Office (Nov. 18, 1682) mandated that confessors are forbidden, even where there would be no revelation direct or indirect, to make any use of the knowledge obtained in the confession that would “displease” the penitent or reveal his identity.
What happens if a priest violates the seal of confession? The Catechism (No. 1467) cites the Code of Canon Law (No. 1388.1) in addressing this issue, which states, “A confessor who directly violates the seal of confession incurs an automatic excommunication reserved to the Apostolic See; if he does so only indirectly, he is to be punished in accord with the seriousness of the offense.” From the severity of the punishment, we can clearly see how sacred the sacramental seal of confession is in the eyes of the Church.
In my own personal experience, rarely, but it has occurred, I have initiated, it has NEVER been initiated to me, a comment with my confessor outside the sacramental seal, referring to some innocuous anecdote, reflecting upon a recent confession; the confessor suddenly develops memory loss, not recalling anything about the sacrament. I suspect/firmly believe this is intentional. Triggered as a reflex, as a protective measure confessors have developed from wisdom and practice. I know to drop it, quickly. I get the message. Gratefully. Thankfully, for the mercy and compassion of these ordained. This has happened more than once, with more than one confessor. Consistently. Such is the seriousness of the matter.
“It is necessary to confess our sins to those to whom the dispensation of God’s mysteries is entrusted. Those doing penance of old are found to have done it before the saints. It is written in the Gospel that they confessed their sins to John the Baptist [Matt. 3:6], but in Acts [19:18] they confessed to the apostles.” –St Basil the Great (Rules Briefly Treated, 288 [A.D. 374])

-relief of torturing of John Sarkander on torturing rack at Sarkander’s gravestone

-reliquary of St Jan Sarkander, Olomouc Cathedral, Czech Republic.
O Mother Mary,
through the memory of your martyred Son
and His servant Jan Sarkander,
we ask you for support for those
whose unfortunate fate is to live
under the rule of violence and hatred.
We ask you to pray for the strength
for them to endure in their faith despite tortures,
plagues and prison. Amen.
Blessed Lent.
Love,
Matthew